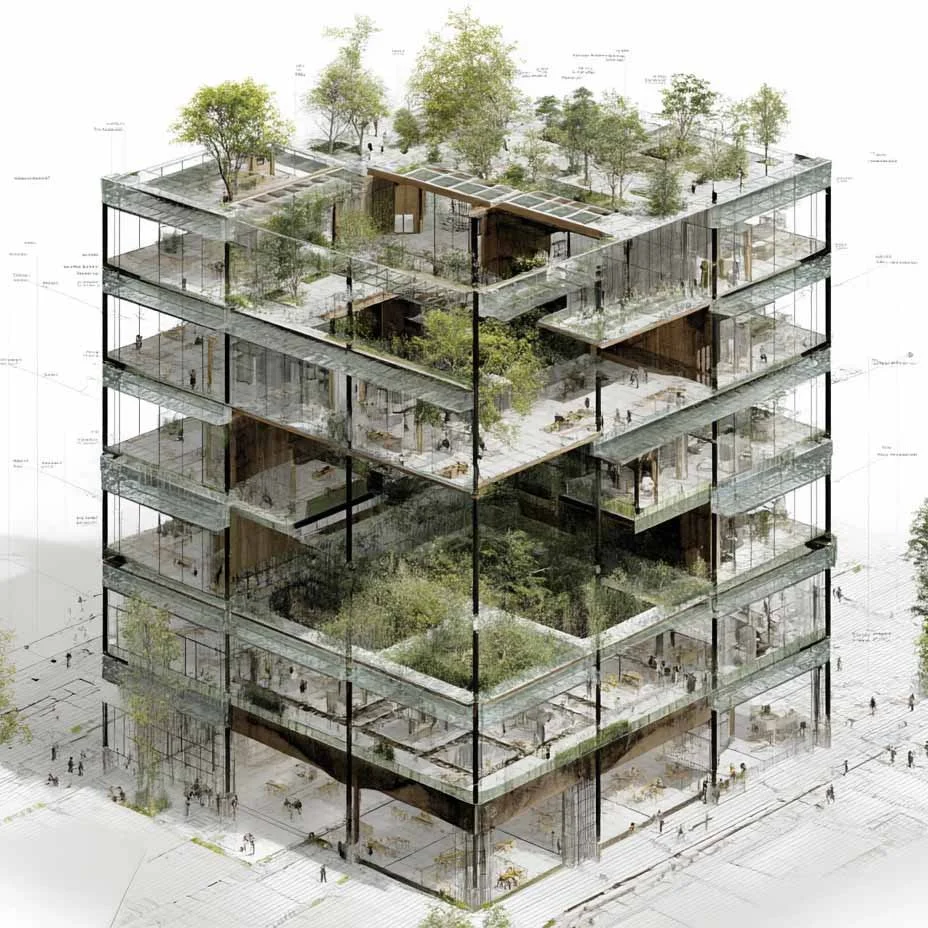
Agritecture: Sustainable Design for Farming in Industrial Buildings
With the world’s population expanding and the need for food rising, it becomes crucial to adopt innovative farming methods. An interesting idea involves transforming existing structures into farming spaces through agriculture-based architecture. This method can boost food output, cut down shipping expenses, and encourage environmentally friendly behaviors. This piece delves into the conversion of buildings into eco-agricultural zones and highlights the advantages for both urban areas and the agricultural sector.
Revitalizing Industrial Structures for Agricultural Purposes
Transformative possibilities exist for repurposing industrial structures due to their open interiors, tall ceilings, and pre-existing infrastructure, ideal conditions for the development of agricultural centers. These spaces can support innovative methods such as vertical farming and hydroponic systems to cultivate crops vertically or without soil, using water enriched with nutrients.
Using hydroponics and aquaponics can reduce water consumption by as much as 90% compared to conventional farming methods, making them well-suited for implementation in existing structures. These systems can also incorporate smart technologies, such as energy-efficient lighting and advanced climate control, to sustain optimal agricultural conditions with minimal energy use.
Plant Chicago, located in Illinois, utilizes hydroponic farming in an industrial setting to grow crops with reduced environmental impact, demonstrating the possibilities of urban agriculture.
Advantages of Cultivating Crops in Urban Structures
Transforming buildings into farming spaces presents a wide range of benefits for both the agricultural sector and urban communities.
Urban agriculture helps decrease the necessity of transporting food over long distances, which in turn significantly reduces carbon emissions. Local farming practices support farm-to-table initiatives by ensuring that produce is cultivated nearby, enhancing freshness and promoting sustainable agriculture.
Urban gardens also play a role in community engagement by offering access to fresh produce and promoting sustainable living habits among local residents.
Many older industrial structures go unused and can benefit from being transformed into community-serving spaces that provide locally sourced food and help minimize urban land waste. Repurposing materials from existing buildings also helps reduce construction waste and supports environmentally friendly building practices.
These farming areas further facilitate the adoption of agricultural technologies. Through data analysis and automation, urban farms can maximize energy use, improve water efficiency, and increase crop yield, paving the way for more sustainable farming practices.
The Challenges of Transforming Spaces for Agriculture
Although agritecture shows great potential for growth and innovation, converting existing structures into viable farming environments comes with its share of challenges.
Launching a farming project inside a building often requires significant upfront investment in specialized equipment and advanced technologies.
Urban Regulations: Current zoning laws might not permit farming activities within certain buildings, requiring adjustments to local ordinances to support these new uses.
Not every industrial building is suitable for farming. Many will require extensive renovations to improve climate control systems, as well as water distribution and lighting infrastructure.
In Summary: Envisioning Urban Spaces for Eco-Farming
Repurposing industrial buildings for agriculture presents a sustainable and effective approach to addressing the increasing need for food production. These renovated spaces help reduce carbon emissions, optimize land use, and enhance local food security. While the process does involve certain challenges, the long-term benefits, such as promoting local food systems and minimizing waste, make urban farming a promising solution for the future.
By incorporating agriculture into repurposed spaces, cities can boost food security, embrace sustainable practices, and increase self-sufficiency within their communities.
Revitalizing Industrial Structures for Agricultural Purposes
Transforming buildings into farming spaces presents a wide range of benefits for both the agricultural sector and urban communities.